Problem at https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/restaurant/problem
Martha is interviewing at Subway. One of the rounds of the interview requires her to cut a bread of size into smaller identical pieces such that each piece is a square having maximum possible side length with no left over piece of bread.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer . lines follow. Each line contains two space separated integers and which denote length and breadth of the bread.
Constraints
Output Format
lines, each containing an integer that denotes the number of squares of maximum size, when the bread is cut as per the given condition.
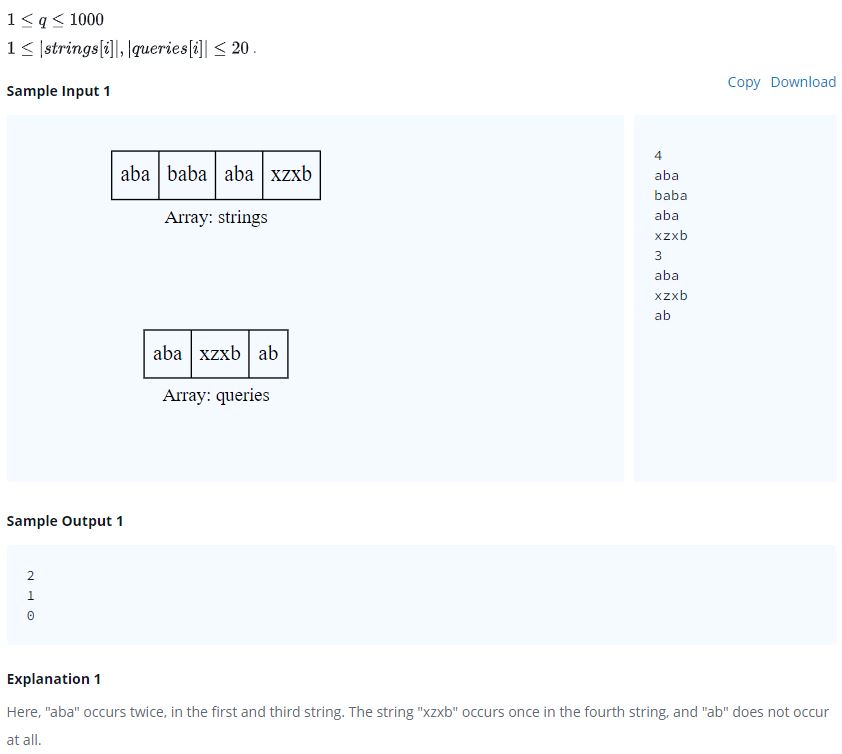
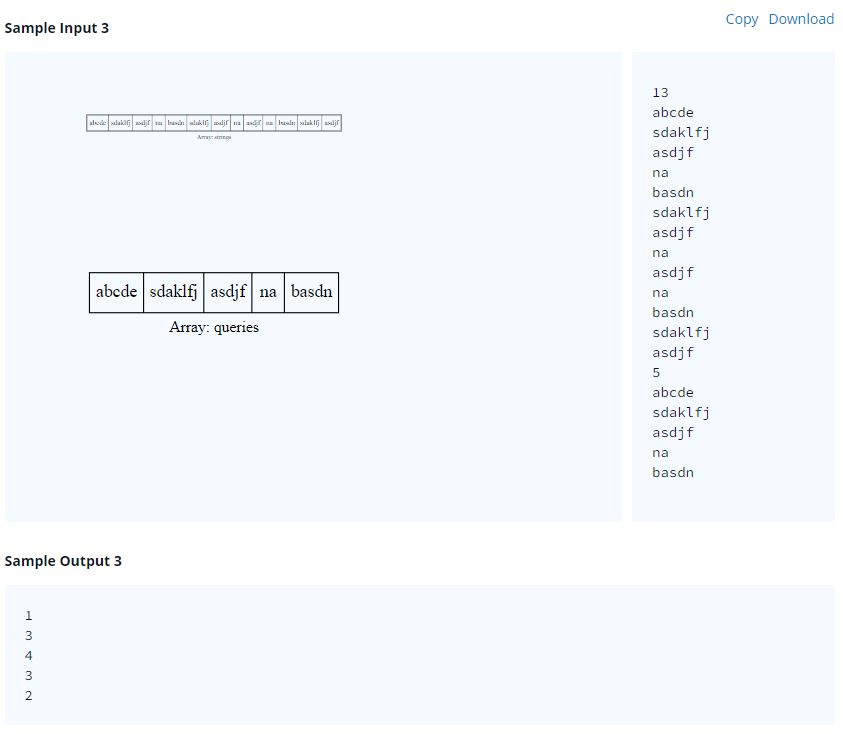
Sample Input 0
2 2 2 6 9
Sample Output 0
1 6
Explanation 0
The 1st testcase has a bread whose original dimensions are , the bread is uncut and is a square. Hence the answer is 1.
The 2nd testcase has a bread of size . We can cut it into 54 squares of size , 6 of size . For other sizes we will have leftovers. Hence, the number of squares of maximum size that can be cut is 6.
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Solution {
/*
* Complete the restaurant function below.
*/
static int restaurant(int l, int b) {
List<Integer> factors = factorsOf(l);
int op = 1;
for(int i:factors) {
if(b%i==0) {
op=i;
}
}
return (l*b)/(op*op);
}
private static List<Integer> factorsOf(int l) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
List<Integer> op = new ArrayList<Integer>();
op.add(1);
for(int i=2;i<=l/2;i++) {
if(l%i==0) {
op.add(i);
}
}
op.add(l);
return op;
}
private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
int t = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])*");
for (int tItr = 0; tItr < t; tItr++) {
String[] lb = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])*");
int l = Integer.parseInt(lb[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(lb[1]);
int result = restaurant(l, b);
bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
bufferedWriter.newLine();
}
bufferedWriter.close();
scanner.close();
}
}